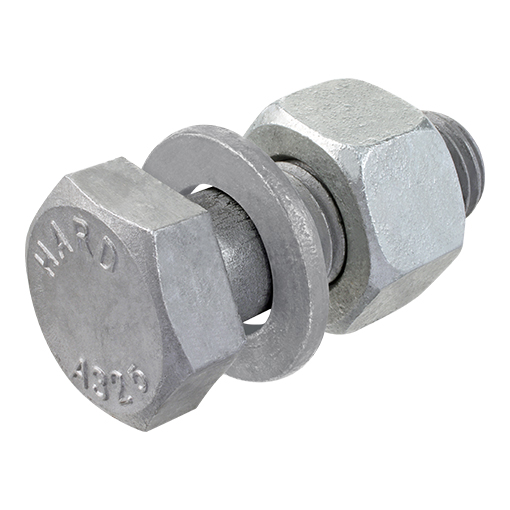
HEAVY HEX NUT ASTM A194 GRADE 2H
| DIAMETER |
THREAD (F.P.P) |
WRENCH |
PACKAGE (PIECE) |
| 1/2” |
13 UNC |
7/8” |
500 |
| 5/8” |
11 UNC |
1.1/16” |
250 |
| 3/4” |
10 UNC |
1.1/4” |
250 |
| 7/8” |
9 UNC |
1.7/16” |
100 |
| 1” |
8 UNC |
1.5/8” |
100 |
FLAT WASHER ASTM F436 TYPE 1
| DIAMETER |
PACKAGE (PIECE) |
| 1/2” |
1000 |
| 5/8” |
1000 |
| 3/4” |
500 |
| 7/8” |
500 |
| 1” |
200 |
HEAVY HEX STRUCTURAL BOLT ASTM A325 TYPE 1
| DIAMETER |
1/2” |
5/8” |
3/4” |
7/8” |
1” |
| THREAD (F.P.P) |
13 UNC |
11 UNC |
10 UNC |
9 UNC |
8 UNC |
| WRENCH |
7/8” |
1.1/16” |
1.1/4” |
1.7/16” |
1.5/8” |
MINIMUM
THREAD LENGTH |
1.1/4” |
1.1/2” |
1.1/2” |
2” |
2.1/4” |
TOTAL
LENGTH |
TYPE OF
THREAD |
PACK. (Piece) |
TYPE OF
THREAD |
PACK. (Piece) |
TYPE OF
THREAD |
PACK. (Piece) |
TYPE OF
THREAD |
PACK. (Piece) |
TYPE OF
THREAD |
PACK. (Piece) |
| 1.1/4” |
TOTAL |
500* |
TOTAL |
250* |
TOTAL |
150* |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| 1.1/2” |
PARTIAL |
400* |
TOTAL |
250* |
TOTAL |
150* |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| 1.3/4” |
PARTIAL |
400* |
PARTIAL |
250* |
PARTIAL |
150* |
TOTAL |
100* |
– |
– |
| 2” |
PARTIAL |
300* |
PARTIAL |
200* |
PARTIAL |
150* |
TOTAL |
100* |
TOTAL |
50 |
| 2.1/4” |
PARTIAL |
300* |
PARTIAL |
200* |
PARTIAL |
100* |
PARTIAL |
100* |
TOTAL |
50 |
| 2.1/2” |
PARTIAL |
300* |
PARTIAL |
200* |
PARTIAL |
100* |
PARTIAL |
50* |
PARTIAL |
50 |
| 2.3/4” |
PARTIAL |
300* |
PARTIAL |
150* |
PARTIAL |
100* |
PARTIAL |
50* |
PARTIAL |
50 |
| 3” |
PARTIAL |
250* |
PARTIAL |
150* |
PARTIAL |
100* |
PARTIAL |
50* |
PARTIAL |
50 |
| 3.1/4” |
– |
– |
PARTIAL |
150* |
PARTIAL |
100* |
PARTIAL |
50* |
PARTIAL |
50 |
| 3.1/2” |
– |
– |
PARTIAL |
150* |
PARTIAL |
100* |
PARTIAL |
50* |
PARTIAL |
50 |
| 3.3/4” |
– |
– |
PARTIAL |
150* |
PARTIAL |
100* |
PARTIAL |
50* |
PARTIAL |
50 |
| 4” |
– |
– |
PARTIAL |
100* |
PARTIAL |
50* |
PARTIAL |
50* |
PARTIAL |
50 |
| 4.1/4” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
PARTIAL |
50* |
PARTIAL |
50 |
| 4.1/2” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
PARTIAL |
50* |
PARTIAL |
25 |
| 4.3/4” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
PARTIAL |
25 |
| 5” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
PARTIAL |
25 |
*All the items are supplied with hot-galvanized coating, in the quantities informed in the tables as units.
COMPOSITION:
Material: Medium carbon steel with quenched tempering
| FINISHING |
LAYER THICKNESS |
RESISTANCE TO CORROSION |
| SALT-SPRAY¹ |
KESTERNICH² |
| HOT GALVANIZED |
50 MICRONS |
N/A³ |
N/A³ |
| WHITE GALVANIZED |
5 MICRONS |
48 HOURS |
N/A³ |
1 – Standards ASTM B117, ABNT NBR 8094 and DIN 50021 (red corrosion).
2 – Standard DIN 50018 (allowing 15% of red corrosion in the bolt head).
3 – Test not applicable. Line ASTM A325 follows, as tightening parameter, the table 16 of standard ABNT NBR 8800.
According to the standard NBR 8800:2008, the bolts tightening control can be made by three processes:
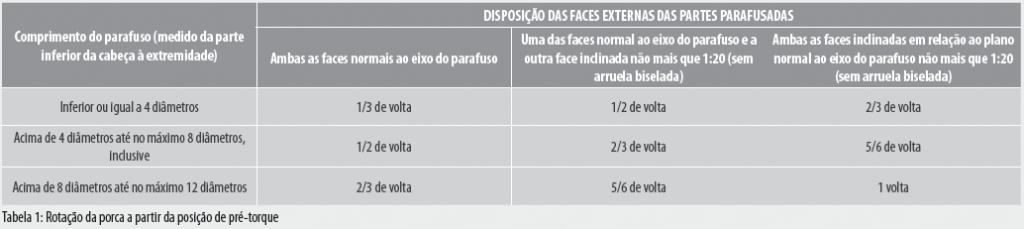
1 – Tightening by the nut revolution: In this method, to apply the minimum prestressing force specified in the Table 15 of standard NBR 8800:2008, there should be a sufficient number of bolts in the pre-torque condition, in order to assure that the parts are in full contact. The pre-torque condition is defined with the tightening obtained after few impacts applied with an impact wrench or by the maximum effort applied by a person using a common wrench. After this initial operation, bolts should be placed in the remaining holes, and also taken to the pre-torque condition. Then, all the bolts are applied with the additional tightening by means of the applicable bolt revolution, as indicated in the Table 1. Both the additional tightening and the final torque is started by the most rigid part of the connection and proceeding toward the free edges. During this operation, the portion opposite to the part that receives the rotation can not spin.
2 – Tightening with calibrated wrench or manual wrench with torque meter: There is no general relationship between the prestressing force in bolts and the torque applied during the nut tightening, due to several factors, including the friction conditions on the surfaces with relative movement. Torque tables based on past experiences or provided in technical literatures can be used.
These wrenches should be adjusted to provide a minimum prestressing 5% higher than the prestressing provided in the Table 15 of standard NBR 8800:2008 and reproduced in the ’’mechanical properties’’ folder. Wrenches should be calibrated at least once at a working day, for each bolt diameter to be installed, and should be recalibrated when significant changes are made in the equipment or when significant differences are observed in the conditions of each surface of the bolts, nuts, and washers. For the other conditions, see item 6.7.4.4.2 of standard NBR 8800:2008.
3 – Tightening using a direct traction indicator: Tightening bolts is allowed using a direct traction indicator, since it is demonstrated that the bolt was subjected to the minimum prestressing force by a direct measurement method established in the Table 15 of standard NBR 8800:2008 and reproduced in the “mechanical properties’’ folder.